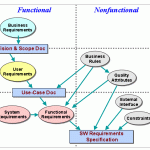
The Functional Requirements Document (FRD) is a formal statement of an application’s functional requirements. It serves the same purpose as a contract. Here, the developers agree to provide the capabilities specified. The client agrees to find the product satisfactory if it provides the capabilities specified in the FRD.
Functional requirements capture the intended behavior of the system. This behavior may be expressed as services, tasks or functions the system is required to perform. The document should be tailored to fit a particular project’s need. They define things such as system calculations, data manipulation and processing, user interface and interaction with the application.
The Functional Requirements Document (FRD) has the following characteristics −
● It demonstrates that the application provides value in terms of the business objectives and business processes in the next few years.
● It contains a complete set of requirements for the application. It leaves no room for anyone to assume anything which is not stated in the FRD.
● It is solution independent. The ERD is a statement of what the application is to do— not of how it works. The FRD does not commit the developers to a design. For that reason, any reference to the use of a specific technology is entirely inappropriate in an FRD.
The functional requirement should include the following −
● Descriptions of data to be entered into the system
● Descriptions of operations performed by each screen
● Descriptions of work-flows performed by the system
● Descriptions of system reports or other outputs
● Who can enter the data into the system?
● How the system meets applicable regulatory requirements?
The functional specification is designed to be read by a general audience. Readers should understand the system, but no technical knowledge should be required to understand this document.

Comments are closed