Meaning
International Business conducts business transactions all over the world. These transactions include the transfer of goods, services, technology, managerial knowledge, and capital to other countries. International business involves exports and imports.
International Business is also known, called or referred as a Global Business or an International Marketing.

An international business has many options for doing business, it includes,
- Exporting goods and services.
- Giving license to produce goods in the host country.
- Starting a joint venture with a company.
- Opening a branch for producing & distributing goods in the host country.
- Providing managerial services to companies in the host country.
Features of International Business
The nature and characteristics or features of international business are:-
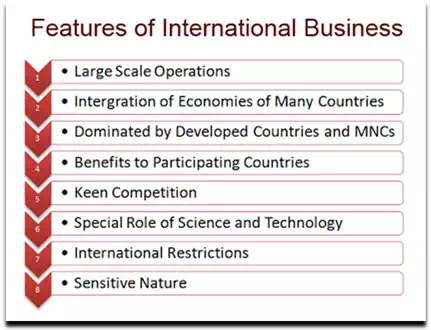
- Large scale operations: In international business, all the operations are conducted on a very huge scale. Production and marketing activities are conducted on a large scale. It first sells its goods in the local market. Then the surplus goods are exported.
- Integration of economies: International business integrates (combines) the economies of many countries. This is because it uses finance from one country, labour from another country, and infrastructure from another country. It designs the product in one country, produces its parts in many different countries and assembles the product in another country. It sells the product in many countries, i.e. in the international market.
- Dominated by developed countries and MNCs: International business is dominated by developed countries and their multinational corporations (MNCs). At present, MNCs from USA, Europe and Japan dominate (fully control) foreign trade. This is because they have large financial and other resources. They also have the best technology and research and development (R & D). They have highly skilled employees and managers because they give very high salaries and other benefits. Therefore, they produce good quality goods and services at low prices. This helps them to capture and dominate the world market.
- Benefits to participating countries: International business gives benefits to all participating countries. However, the developed (rich) countries get the maximum benefits. The developing (poor) countries also get benefits. They get foreign capital and technology. They get rapid industrial development. They get more employment opportunities. All this results in economic development of the developing countries. Therefore, developing countries open up their economies through liberal economic policies.
- Keen competition: International business has to face keen (too much) competition in the world market. The competition is between unequal partners i.e. developed and developing countries. In this keen competition, developed countries and their MNCs are in a favourable position because they produce superior quality goods and services at very low prices. Developed countries also have many contacts in the world market. So, developing countries find it very difficult to face competition from developed countries.
- Special role of science and technology: International business gives a lot of importance to science and technology. Science and Technology (S & T) help the business to have large-scale production. Developed countries use high technologies. Therefore, they dominate global business. International business helps them to transfer such top high-end technologies to the developing countries.
- International restrictions: International business faces many restrictions on the inflow and outflow of capital, technology and goods. Many governments do not allow international businesses to enter their countries. They have many trade blocks, tariff barriers, foreign exchange restrictions, etc. All this is harmful to international business.
- Sensitive nature: The international business is very sensitive in nature. Any changes in the economic policies, technology, political environment, etc. has a huge impact on it. Therefore, international business must conduct marketing research to find out and study these changes. They must adjust their business activities and adapt accordingly to survive changes.


