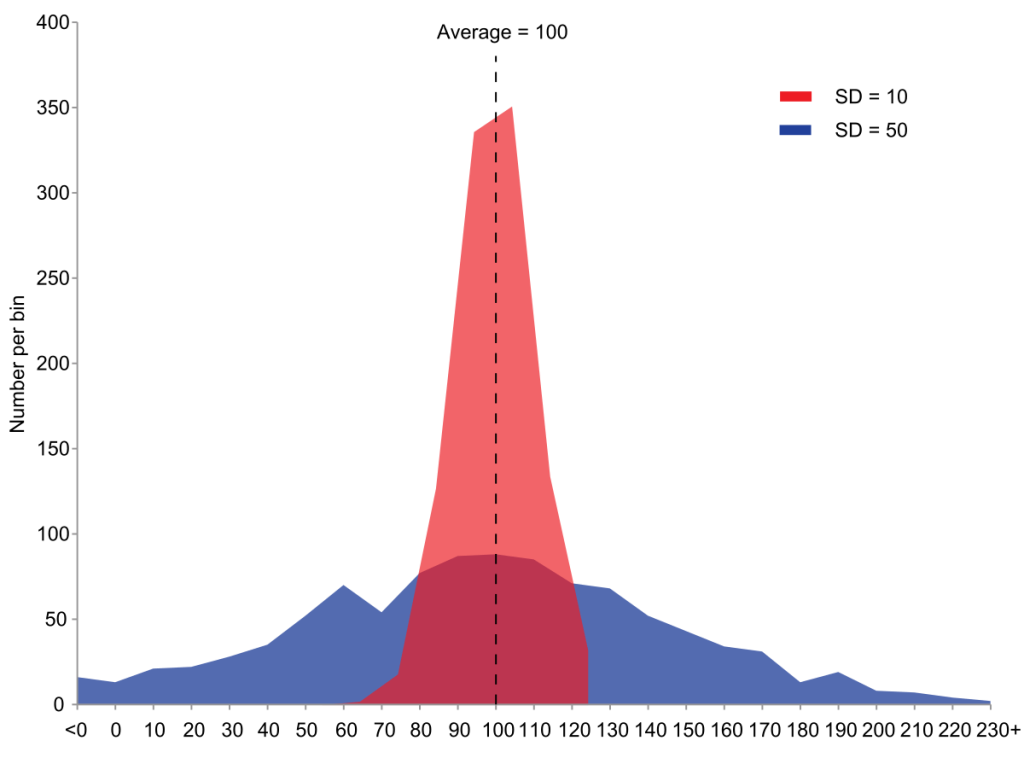
A variance is defined as the average of Squared differences from mean value.
Combination is defined and given by the following function:
Formula
δ=∑(M−ni)2nδ=∑(M−ni)2n
Where −
· MM = Mean of items.
· nn = the number of items considered.
· nini = items.
Example
Problem Statement:
Find the variance between following data : {600, 470, 170, 430, 300}
Solution:
Step 1: Determine the Mean of the given items.
M=600+470+170+430+3005=19705=394M=600+470+170+430+3005=19705=394
Step 2: Determine Variance
δ=∑(M−ni)2n=(600−394)2+(470−394)2+(170−394)2+(430−394)2+(300−394)25=(206)2+(76)2+(−224)2+(36)2+(−94)25=42,436+5,776+50,176+1,296+8,8365=108,5205=(14)(13)(3)(11)(2)(1)=21,704δ=∑(M−ni)2n=(600−394)2+(470−394)2+(170−394)2+(430−394)2+(300−394)25=(206)2+(76)2+(−224)2+(36)2+(−94)25=42,436+5,776+50,176+1,296+8,8365=108,5205=(14)(13)(3)(11)(2)(1)=21,704
As a result, Variance is 21,70421,704.