Definition of Economic Growth
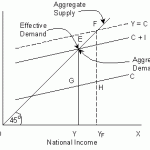
Economic growth refers to an increase in the goods and services produced by an economy over a particular period of time. It is measured as a percentage increase in real gross domestic product which is GDP adjusted to inflation. GDP is the market value for all the final goods and services produced in an economy.
Theories of Economic Growth
The Classical Approach
Adam Smith laid emphasis on increasing returns as a source of economic growth. He focused on foreign trade to widen the market and raise productivity of trading countries. Trade enables a country to buy goods from abroad at a lower cost as compared to which they can be produced in the home country.
In modern growth theory, Lucas has strongly emphasized the role of increasing returns through direct foreign investment which encourages learning by doing through knowledge capital. In Southeast Asia, the newly industrialized countries (NICs) have achieved very high growth rates in the last two decades.
The Neoclassical Approach
The neoclassical approach to economic growth has been divided into two sections −
● The first section is the competitive model of Walrasian equilibrium where markets play a very crucial role in allocating the resources effectively. To secure the optimal allocation of inputs and outputs, markets for labor, finance and capital have been used. This type of competitive paradigm was used by Solow to develop a growth model.
● The second section of the neoclassical model assumes that technology is given. Solow used the interpretation that technology in the production function is superficial. The point is that R&D investment and human capital through learning by doing were not explicitly recognized.
The neoclassical growth model developed by Solow fails to explain the fact of actual growth behavior. This failure is caused due to the model’s prediction that per capita output approaches a steady state path along which it grows at a rate that is given. This means that the long-term rate of national growth is determined outside the model and is independent of preferences and most aspects of the production function and policy measures.
The Modern Approach
The modern approach to market comprises of several features. The new economy emerging today is spreading all over the world. It is a revolution in knowledge capital and information explosion. Following are the important key elements −
● Innovation theory by Schumpeter, inter firm and inter industry diffusion of knowledge.
● Increasing efficiency of the telecommunications and micro-computer industry.
● Global expansion of trade through modern externalities and networks.
Modern theory of economic growth focuses mainly on two channels of inducing growth through expenses spent on research and development on the core component of knowledge innovations. First channel is the impact on the available goods and services and the other one is the impact on the stock of knowledge phenomena.