The Rayleigh distribution is a distribution of continuous probability density function. It is named after the English Lord Rayleigh. This distribution is widely used for the following:
· Communications – to model multiple paths of densely scattered signals while reaching a receiver.
· Physical Sciences – to model wind speed, wave heights, sound or light radiation.
· Engineering – to check the lifetime of an object depending upon its age.
· Medical Imaging – to model noise variance in magnetic resonance imaging.
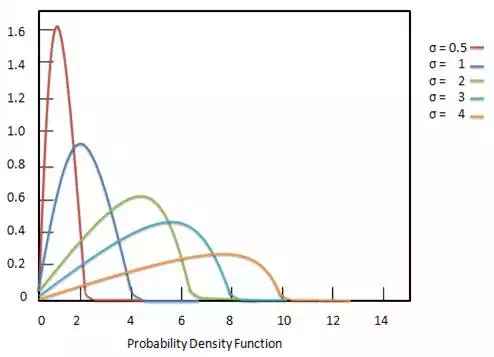
The probability density function Rayleigh distribution is defined as:
Formula
f(x;σ)=xσ2e−x22σ2,x≥0f(x;σ)=xσ2e−x22σ2,x≥0
Where −
· σσ = scale parameter of the distribution.
The comulative distribution function Rayleigh distribution is defined as:
Formula
F(x;σ)=1−e−x22σ2,x∈[0∞F(x;σ)=1−e−x22σ2,x∈[0∞
Where −
· σσ = scale parameter of the distribution.
Variance and Expected Value
The expected value or the mean of a Rayleigh distribution is given by:
E[x]=σπ2−−√E[x]=σπ2
The variance of a Rayleigh distribution is given by:
Var[x]=σ24−π2