In this chapter, let us understand the process of performance management. Performance management is a process management which consists of the following activities −
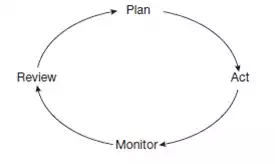
● Plan − decide what to do and how to do it.
● Act − carry out the work needed to implement the plan.
● Monitor − carry out continuous checks on what is being done and measure outcomes in order to assess progress in implementing the plan.
● Review − consider what has been achieved and, in the light of this, establish what more needs to be done and any corrective action required if performance is not in line with the plan.
This sequence of activities can be expressed as a continuous cycle as shown in the following figure −
Performance Management Cycle
Performance management can be described as a continuous process cycle as shown in the following figure, which follows the plan–act–monitor–review sequence as described above.
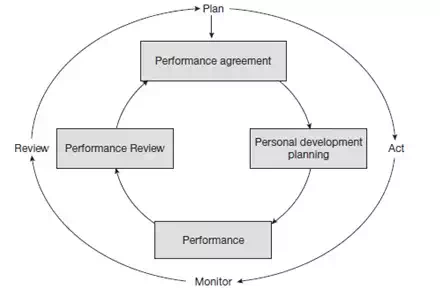
Performance Management Sequence
The sequence of processes carried out in this cycle and the likely outcomes are illustrated in the following figure −
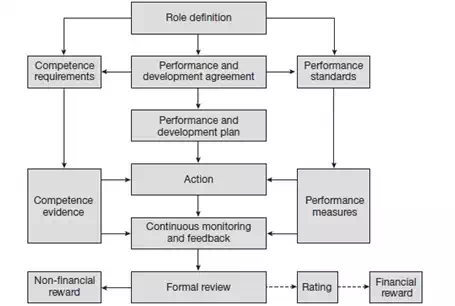
Performance Management Activities
Let us now discuss the activities that take place in performance management. The main activities are −
● Role definition, in which the key result areas and competence requirements are agreed.
● The performance agreement, which defines expectations − what individuals have to achieve in the form of objectives, how performance will be measured and the competences needed to deliver the required results.
● The performance improvement plan, which specifies what individuals should do to improve their performance when necessary.
● The personal development plan, which sets out the actions people should take to develop their knowledge and skills and increase their levels of competence.
● Managing performance throughout the year, when action is taken to implement the performance agreement and performance improvement and personal development plans as individuals carry on with their day-to-day work and their planned learning activities. It includes a continuous process of providing feedback on performance, conducting informal progress reviews, updated objectives and, where necessary, dealing with performance problems.
● Performance review is an evaluation stage, where a review of performance over a period takes place covering the aspects like achievements, progress and problems as the basis for the next part of the continuous cycle – a revised performance agreement and performance improvement and personal development plans. It can also lead to performance ratings.

Performance Management in Action
Performance management should not be like a system based on periodical formal appraisals and detailed documentation. The activities should be logical in the sense of contributing to an overall approach in which all aspects of the performance management process are designed.
Thus, in every organization there is a need to declare why performance management is important, how it works and how people will be affected by it. The declaration should have the visible and continuous support of top management and should emphasize to develop a high-performance culture and integrate organizational and individual goals.
Performance management recognizes the fact that we all create the view of the people who work for the organization and it also makes sense to express that view explicitly against a framework of reference.

