The beta distribution represents continuous probability distribution parametrized by two positive shape parameters, αα and ββ, which appear as exponents of the random variable x and control the shape of the distribution.
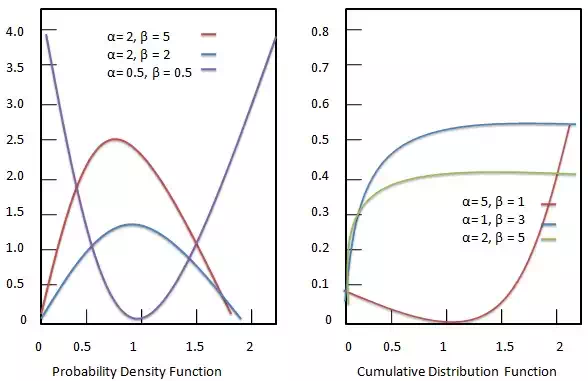
Probability density function
Probability density function of Beta distribution is given as:
Formula
f(x)=(x−a)α−1(b−x)β−1B(α,β)(b−a)α+β−1a≤x≤b;α,β>0where B(α,β)=∫10tα−1(1−t)β−1dtf(x)=(x−a)α−1(b−x)β−1B(α,β)(b−a)α+β−1a≤x≤b;α,β>0where B(α,β)=∫01tα−1(1−t)β−1dt
Where −
· α,βα,β = shape parameters.
· a,ba,b = upper and lower bounds.
· B(α,β)B(α,β) = Beta function.
Standard Beta Distribution
In case of having upper and lower bounds as 1 and 0, beta distribution is called the standard beta distribution. It is driven by following formula:
Formula
f(x)=xα−1(1−x)β−1B(α,β)≤x≤1;α,β>0f(x)=xα−1(1−x)β−1B(α,β)≤x≤1;α,β>0
Cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function of Beta distribution is given as:
Formula
F(x)=Ix(α,β)=∫x0tα−1(1−t)β−1dtB(α,β)0≤x≤1;p,β>0F(x)=Ix(α,β)=∫0xtα−1(1−t)β−1dtB(α,β)0≤x≤1;p,β>0
Where −
· α,βα,β = shape parameters.
· a,ba,b = upper and lower bounds.
· B(α,β)B(α,β) = Beta function.
It is also called incomplete beta function ratio.